The Four Functions of Management: Key to Business Success
Management is the backbone of every successful business, and knowing its functions can prove to be essential in fulfilling your goals. In this guide, we get into the four functions of management and give them a manageable breakdown that anyone trying to climb the ladder from aspiring or new managers to seasoned pros can take something away from in our modern-era workplace.
Get implemented the management strategies by the end of this article by providing you with directions to figure this out in your organization.
What are the Four Functions of Management?
Overview of the Key Functions
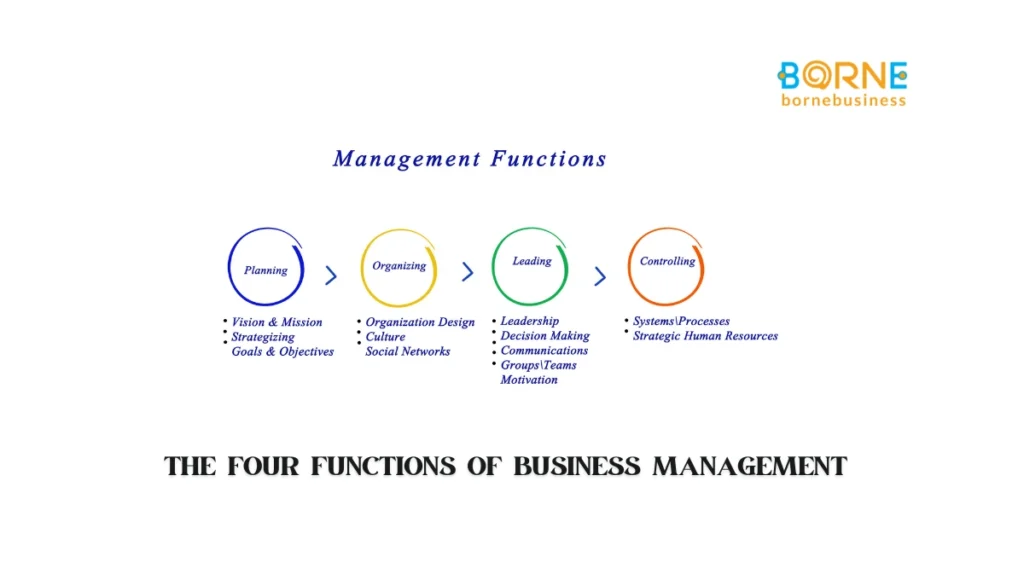
The four functions of management planning, organizing, leading, and controlling—are widely acknowledged to be essential building blocks of effective management. This trio represents a process that enables managers to organize functions, ensure resources are in alignment, and accomplish organizational objectives effectively.
These functions do not function in isolation, they complement each other to offer a dynamic and seamless management process.
Planning prepares the ground by outlining desired outcomes and mapping out all possible approaches to accomplishing them.
Organizing takes those plans and puts them into action, coordinating resources and activities to ensure smooth delivery.
Leading is the practice of encouraging and directing employees to help them remain on course with the company objectives.
Controlling, on the other hand, keeps progress in line with objectives through performance tracking and adjustments.
Whether it involves the distribution of resources, establishing a conducive working environment or reacting to surprises in a situation, these essential functions are the real sources of power with which managers can make prudent decision-making towards organizational success.
Why Are These Services Critical to Business?
We need to ensure the long-term vision and day-to-day operations are balanced but in the right market, it can be hard to do. Organizations strike this balance through the four functions of management.
The first step to effective management is providing clear goals which provide a map for the entire organization to follow. Managers coordinate closely so every department, team, and even individual employee knows how to work toward these goals.
They also create the right conditions for employees to be motivated, directed, and supported, which is crucial for productivity. This continual process of planning-organizing-leading-controlling helps businesses deal with paradox, manage and tackle challenges, and enables them to stay ahead in the cut-throat competition prevailing in modern business dynamics (Gilley et.al, 2006).
Fostering these functions is not just essential for any organization to succeed, but also helps organizations achieve sustainable growth in changing times.

Planning: The Beginning of the Management Process
The importance of the Planning function
Planning is the foundation of management, being the first and most important step in the management process. In this stage, managers outline what the organization wants and develop a strategic plan with specific details about how to get there. This involves things such as determining priorities and forecasting possible challenges, along with what resources will be of use for success.
Planning effectively is not only about setting targets — all your decisions should lead towards reaching wider business objectives for the organization. In this phase, managers have to make decisions by looking at options and recognizing which one of them is the best route for the organization in terms of short-term as well as long-term goals. This initiative allows businesses to deal with unknowns in a methodical way and capitalize on opportunities.
Strategic and Tactical Planning: The Backbone of What You’ll Work Towards
There are two levels of planning: strategic and tactical.
Strategic planning looks at the 30,000-foot view. It outlines the company’s long-term goals, including growth in the marketplace, brand positioning, or innovation objectives. This kind of planning is done by top management that ties all the departments to provide services toward a common goal or vision.
In contrast, tactical planning takes these high-level strategies and translates them into specific, short-term objectives that can be executed over a defined period of time. This is focused on department or project-level initiatives, allowing middle management and non-executive dept managers to cascade strategy into their teams.
These planning levels work in tandem to ensure a smooth link from the vision of the organization down to day-to-day operations. Both strategic and tactical planning instill a sense of focus and clarity into the organization, allowing team members to be clear on how they can contribute to achieving the company goals.
Together, these two approaches help organizations coordinate resources, make more effective processes, and find a road to success. This dual emphasis not only maximizes efficiency; it allows organizations to pivot on changing market conditions whilst ensuring the balance between short-term wins and long-term goals are met.

Planning for Tracks: Making It All Happen
What Is the Organizing Function about?
You plan for action, and the organizing function is when these plans take shape. Human, financial, and physical resources must be organized and coordinated in order to put the distilled strategic plan into effect.
Managers are concerned with creating flows so that tasks can be done, hierarchies published, and roles defined.
A crucial part of this function is how to establish an organizational structure that allows clear communication and optimal resource allocation. From assigning roles to functioning departmental or interdepartmental, the organizing function makes sure that all parts of the organization move along harmoniously.
In this phase, the broad objectives established during planning become specific actions that stimulate progress.
Building an Effective Organizational Structure
For business objectives, an efficient model is really important. This requires thoughtful resource allocation from managers to secure the necessary tools, information, and support for each team member to succeed. Providing the training, technology, and other essentials necessary for success.
An important tenth factor in the organization is delegating tasks. It is up to managers to assign tasks in accordance with every employee’s strengths, or area of expertise, and capacity. This allows them to distribute workload evenly and avoid process shrinkages. When done correctly, delegation gives your employees the confidence they need to excel at their jobs and helps them take a sense of ownership over their work.
It also cultivates a positive company culture where communication is less hindered and employees are aware of how their work fits into the bigger picture.
A well-organized and prepared team means that businesses are, in turn, better able to meet their organizational aims and goals; staying productive while also pivoting within a changing landscape, both internal or otherwise.
What organizing does in kind of a roundabout way is it connects the planning and doing aspects of management, providing a basis for other functions to flow from and be done upon for success within an organization.

Leading: Motivating and Advising Teams
What is the purpose of management and also exploring its leading function
The leading function of management involves motivating, guiding, and influencing employees to work hard to achieve organizational goals.
Effective leadership is more than handing out tasks; it is making sure everyone rowing the same way, instilling trust and a sense of purpose among team members. Motivating employees is one of the key elements in ensuring the success of an organization and directly reflects on the morale, productivity, and engagement of its people.
Well-founded leadership capabilities are important and necessary for organizational diversity management and team collaboration. The skills involved are open communication, listening, and flexibility.
Leaders must also create a positive work culture, one where employees feel appreciated and supported in contributing their unique abilities to the overall goals of the organization.
How and why Leadership Style plays a part in motivating employees
The manager’s style of leadership plays a significant role in motivating employees and improving overall performance. Leadership is not a universal thing the best managers adjust their style according to their team, task, and work context.
For example:
An incredibly strict, back-to-the-basics approach works when there is a need for direction and protocol – such as with clear processes that absolutely must be followed word-for-word.
The participative style, where employees are involved in decision-making and the process is collaborative, leads to innovation and greater ownership of outcomes among team members.
In a transformational leadership style, which is oriented to find inspiration in the employees while making them challenge for growth; it creates a highly energetic unit.
Any style of management is possibly the best that will achieve routine delivery of organizational objectives if only one understands the strengths, challenges, and motivations of their team. In addition, effective leaders achieve the right mix of process and freedom, making sure that team members are both directed and autonomous.
At the end of it all, the foremost thing about being a leader is ensuring that you set everyone working in the same direction and toward achieving common business goals. This flexible leadership style offers a system in which employees are not merely managed but motivated to achieve their best work, creating both immediate wins and sustained success.
Controlling: Ensuring Goals Are Met
How the Controlling Function Looks
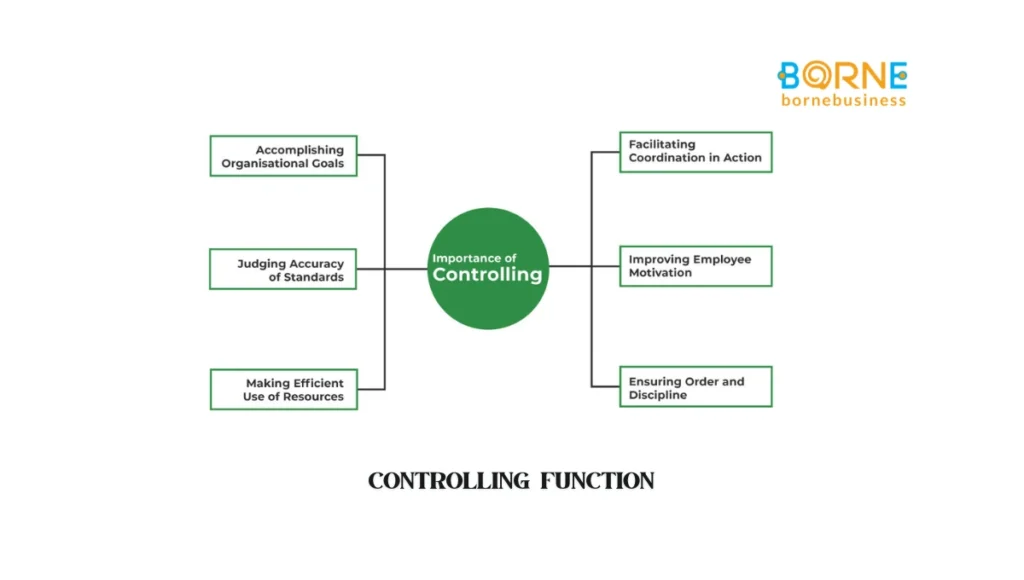
This control is crucial for an organization as it ensures they are following the path and way they are supposed to from the beginning. It encompasses tracking progress, evaluating results, and tweaking plans to ensure goals are met efficiently.
This is the function that managers use to compare what has actually occurred against their goals show the gaps and work on those problems that lead them toward corrections.
It involves analyzing important benchmarks, outlining firm standards of output, and creating a way to gauge development at regular intervals. Control is the checkpoint in the management process to ensure that every action is consistent with the strategy and tactical plans for which the organization was designed.
Regardless of whether you are maintaining the day-to-day workings of an organization or evaluating long-term strategies, keeping control is essential in both retaining success and for organizational flexibility.
Using Metrics and Standards of Performance for Good Management
As such, this enables managers to hold their teams to a high degree of accountability and transparency throughout the organization with the use of clearly defined metrics and performance standards. They are also providing measurable benchmarks that allow teams to determine whether or not they are on track for success.
For example:
Productivity metrics demonstrate how well resources are being utilized.
Quality standards guarantee that products or services meet customer requirements.
Fiscal responsibility is tracked through financial metrics such as budget adherence.
Evaluation on a regular basis does not only highlight areas that require corrective action but also offers the chance to identify and reward good performance. This two-pronged method inspires a culture of ongoing growth while keeping employees motivated.
In the controlling function, project management tools help managers optimize workflows with respect to monitoring deadlines and tracking human resources.
Thirdly, good communication guarantees that team members know what is expected from them in terms of performance and if there are any issues and or changes that need to be made to meet objectives.
As problems emerge with the products, managers need to take quick action with specific corrective actions: changing resources, and processes. This way ensures momentum continues as the changing landscape requires swift action to ensure progress towards strategic objectives.
Styling it The controlling function is not just about monitoring, it is a dynamic system of ensuring that the organization always moves towards its mission, enhances accountability, and creates resilience against hurdles. Through mastery of this function, managers ensure that each endeavor is a step toward desired results; thus cementing success for the organization in the business market.
Management and Its Importance in the Business World
Coordinate deliberately through the entire organization
Management is not just something you do to run a business; rather it is an organized field of study that makes certain the entire hierarchy in a company is driving towards one big vision. An important task for managers is to align objectives — the manager has to be the link between the strategic vision of an organization and the basic operational tasks done by employees.
Setting clear, measurable goals at all levels from individual team members to department to organization-wide allows managers to create a strategy that works together and builds off one another.
Such alignment makes sure that everything, from tactical decision-making to long-term initiatives, supports the broader business goals.
Good alignment is not only about clearly communicating the goals but also ensuring that everyone understands what they are working toward and how to achieve success. It also means changing the strategies used to meet those objectives to fit new conditions while still accomplishing organizational goals.
Management Functions and Relationship with Business Performance
The four functions of management planning, organizing, leading, and controlling—provide a comprehensive framework for organizational success. From the effective implementation of these functions, we can reach:
Better performance: Managers rearrange their processes and leverage human resources to maintain efficiency and productivity at all levels of the organization.
Increased Employee Satisfaction: Proper leadership, sound policies, and a positive work environment lead to motivated employees who are invested in your vision.
Reaching of business objectives: The integration of the management functions brings all activities in line with the vision of the organization and makes success sustainable.
With the technological advancements, global competition, and changing consumer expectations of modern business like never before there is a lot for Management to handle. Automation of core management functions helps organizations to be agile and competitive, and adjust as required for any change while also ensuring the focus remains on target objectives.
In the end, management is about bringing together people, processes, and resources to serve not just short-term goals but also long-term growth and sustainability. This link between how well you manage your business and the success or failure of that business speaks to why great managerial practices are essential in the field of modern business, which is often rapidly changing.

How to Be a Manager — The Ultimate Guide
Essential Managerial Skills to be Nurtured
As a manager, you have to get the basics of management under your belt. Some of the top ones are decision-making, effective communication, and strategic thinking. Making decisions is one of the most important tasks performed by managers, so effective ones are skilled in applying both intuitive and rational analysis to business decisions.
Communication, of course, is another important part of the puzzle because teams need to know what they should be working on; they need feedback, and they want to know that their efforts are appreciated. A good communicator leader will create similar transparency and collaboration with the team which is a must for success.
Strategic thinking also enables managers to step beyond the narrow tasks before them, foresee looming issues, and design strategies for lasting productivity and growth. Together these abilities lay the groundwork for a successful career in management.
Adjusting to the Nuances Of Contemporary Business
Today, the business environment is characterized by change, technology, and customer demands. In order to be still a productive player, a manager must navigate through these complexities.
This means using contemporary tools such as project management and statistical analysis software to remain organized and help maximize decision-making.
Also, there is an ongoing education part. Management can gain the flexibility to deal with change by keeping abreast of new management practices and availing training and information about what is being done in the industry.
This method not only equips managers to be effective but also keeps their teams aligned with new strategies and technologies for lasting business success.

